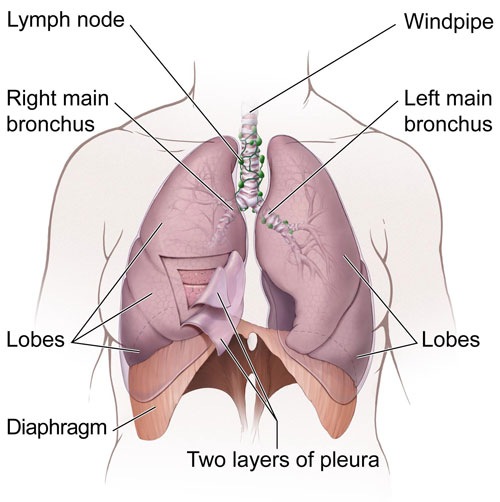
More than 40,000 people in the UK are diagnosed with lung cancer each year, making it a common and deadly kind of the disease. Lung cancer does not initially exhibit any symptoms, but when they eventually occur, they typically include the following:
exhaling blood
ongoing cough
breathing difficulty
Unaccounted-for weight loss
Unfounded sluggishness and exhaustion
Coughing or heavy breathing causes pain.
lung cancer types
Lung cancer can develop in two different ways:
Lung cancer that develops from the lung tissue is referred to as primary lung cancer.
Cancer that begins in one area of the body but spreads to the lung tissue is referred to as secondary lung cancer.
first-stage lung cancer
Based on the types of cells affected, primary lung cancer is further divided into two major groups. They consist of:
Around 80% of occurrences of lung cancer are non-small-cell lung cancer, making it the most prevalent type. Non-small-cell lung cancer can be classified into the following categories based on which cells are affected by the disease:
cancer of the squamous cell
Adenocarcinoma
Cancer of the large cell. Lung cancer is rare among people aged under 40 years. The incidence of lung cancer rises sharply as people age and is most common among those aged between 70 and 75 years. One of the main causes of lung cancer is cigarette smoking, which is the causative factor in around 90% of patients. Smokers regularly inhale a variety of toxic substances, which increases the risk of developing the condition. However, non-smokers can also develop lung cancer.
The treatment of lung cancer depends on which type of cancer a patient has, how far the cancer has progressed and the patient’s general state of health. When diagnosed early and if the cancer cells are confined to one small area, the cancer is usually surgically removed. In cases where surgery is not considered an appropriate option due to a poor health status, radiotherapy may be the advised treatment approach. In cases where the cancer is too far advanced to be treated with surgery or radiotherapy, chemotherapy may be prescribed instead.